HCVTyper: A Nextflow pipeline for hepatitis C virus genome assembly, genotyping and antiviral resistance detection
Bråte, J., Instefjord, K, H., Alfsnes, K. and Stene-Johansen, K. 2025. bioRxiv. doi:https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.10.21.683612
Abstract
Motivation
High-throughput sequencing is increasingly used for the characterization of hepatitis C virus (HCV), enabling genotyping, detection of mixed infections, and identification of resistance-associated variants (RAVs). However, the bioinformatics analysis of capture-based or metagenomic HCV datasets remains challenging due to high genome diversity, co-infections, and the need for reproducible workflows.
Results
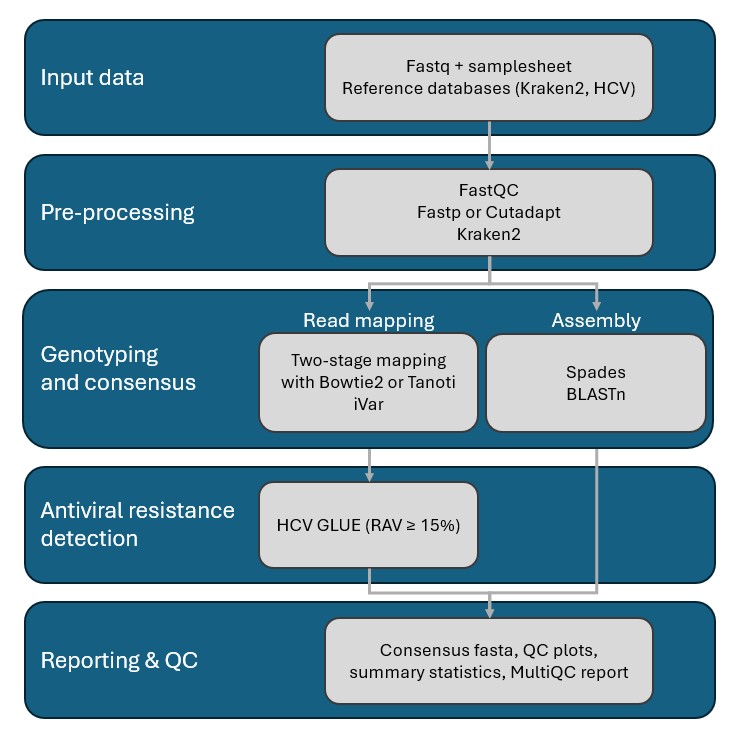
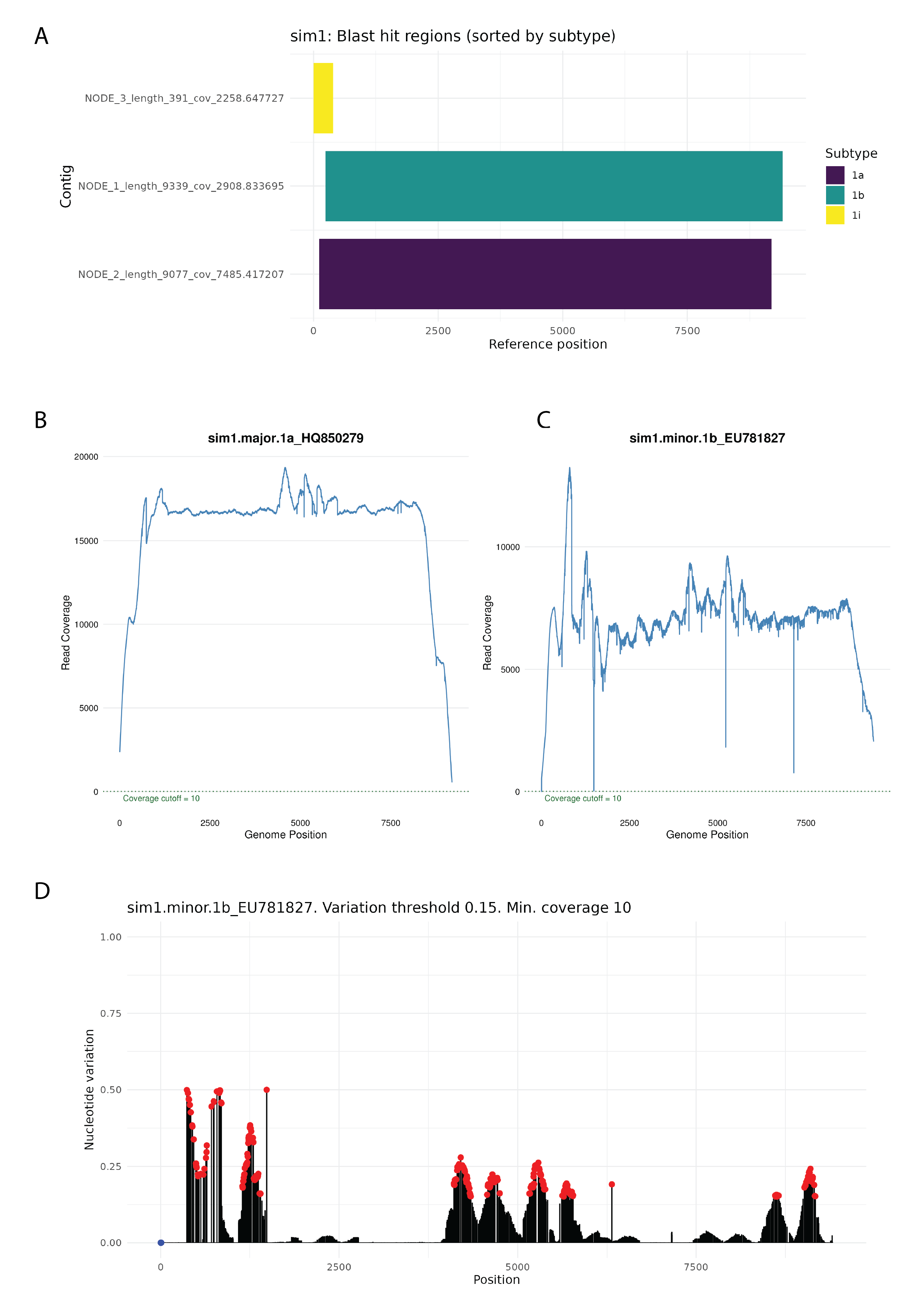
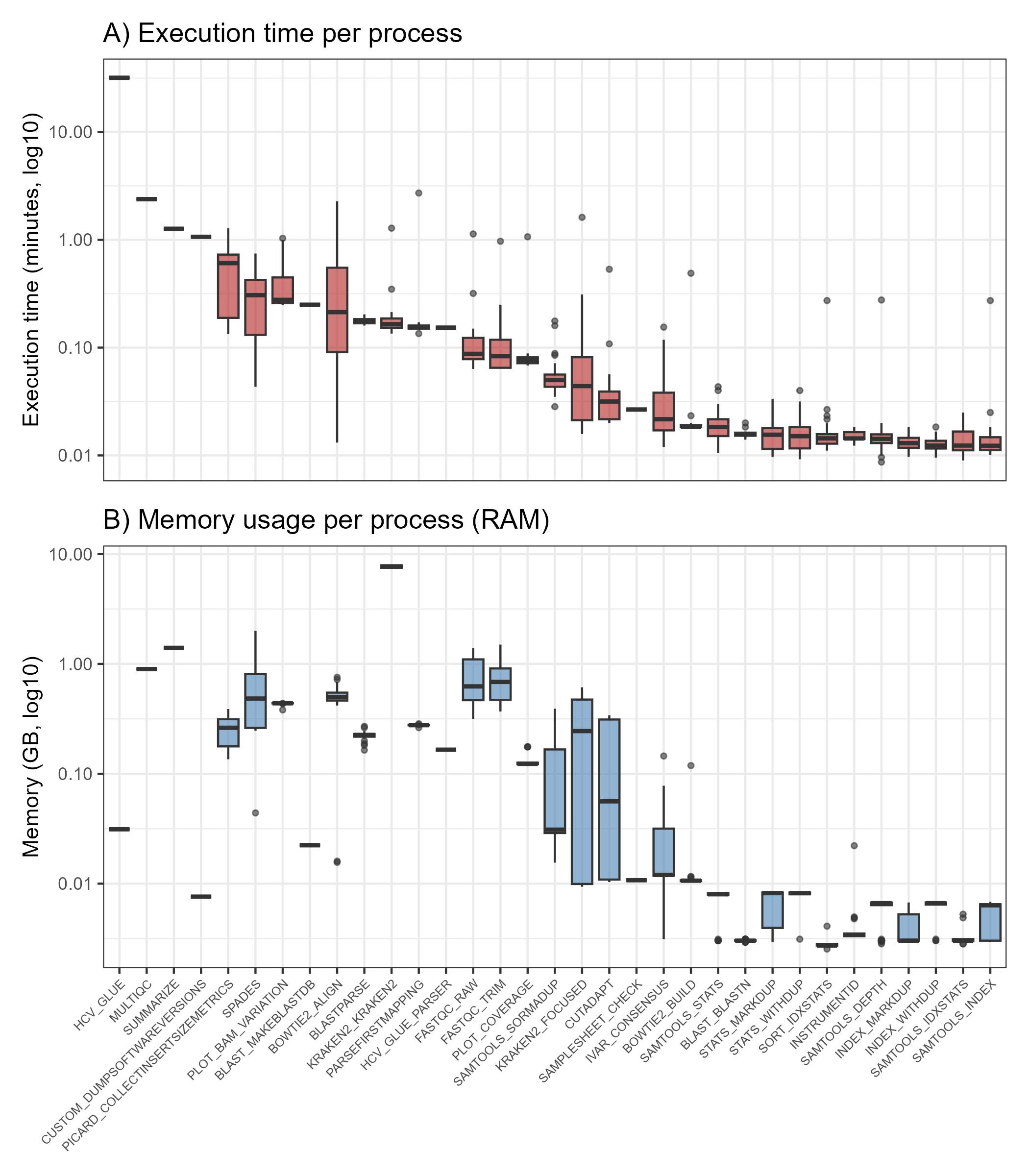
We present HCVTyper, a reproducible bioinformatics pipeline for HCV genome analysis implemented in Nextflow. HCVTyper integrates quality control, taxonomic classification, two-step reference-based mapping, consensus generation, de novo assembly, and antiviral resistance annotation. Benchmarking with simulated mixtures and real-world datasets demonstrated robust identification of both major and minor genotypes across a wide abundance range, with user-adjustable thresholds for co-infection detection. Integration with HCV-GLUE enables sensitive detection of RAVs from mapping files, including low-frequency variants. The pipeline is fully containerized (Docker) and produces comprehensive reports to facilitate interpretation.
Availability and implementation
HCVTyper is open-source and available at: https://github.com/folkehelseinstituttet/hcvtyper
Contact jon.brate{at}fhi.no